Do not assume this technology is out of your reach because of limited resources and costs. The value and benefit of model-informed precision dosing software is huge, and it pays for itself rather quickly.
- Kimberly Askren, PharmD at Boone County Hospital
Opportunity
Boone County Hospital, a 25-bed critical access facility serving a rural Iowa community, faced the challenge of managing complex antibiotic therapy with limited staff and resources. Their traditional approach required two timed blood draws and manual PK calculations (both labor-intensive and prone to variability). Compounding the risk, new national consensus guidelines increasingly favored AUC/MIC-based monitoring over trough-based methods, and called for Bayesian modeling to meet evolving standards.1 For a small hospital, the stakes were high: reduced adverse events, better antibiotic efficacy, and workflow efficiency were critical to patient safety and financial sustainability.
Solution
In May 2019, Boone County adopted the InsightRX Nova precision dosing platform across four high-priority antibiotics, including vancomycin. By incorporating patient-specific data and Bayesian forecasting, the software allowed clinicians to calculate individualized dosing from a single scheduled lab draw, replacing the previous two-sample, steady-state manual workflows. InsightRX also provided analytics to track performance against targets and support antimicrobial stewardship mandates.
We evaluated three different Bayesian analytics precision dosing vendors. In the end, we chose the one that provided the best customer service and the most user-friendly platform for our specific users.
- Kimberly Askren, PharmD at Boone County Hospital
Impact
Implementing InsightRX delivered real, practical change in Boone County’s day-to-day operations. Clinicians no longer needed to coordinate special timing for labs; doses were computed rapidly with confidence. Workflows became leaner, clinician time was reallocated to more valuable tasks, and patients experienced fewer invasive lab draws:
- A streamlined monitoring protocol replaced the old two-draw manual approach
- Dose calculations shifted from manual spreadsheets to automated Bayesian models
- The platform’s analytics supported performance tracking for stewardship compliance
Results
Implementation helped lead to a reduction in acute kidney injury events
Over approximately 50 vancomycin patients per year, Boone County saw zero nephrotoxicity events following deployment in the first year — a remarkable achievement. Because the software allows pharmacists to better target appropriate regimens for patients, clinicians are empowered to make decisions which more easily avoid instances of supra-therapeutic dosing.
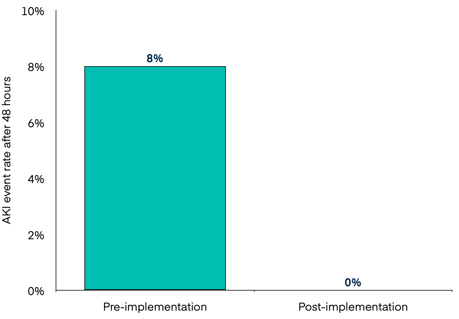
Figure 1 shows AKI event rates pre- and post-implementation of Bayesian MIPD with InsightRX Nova for vancomycin AUC dosing.
Pharmacists were able to better achieve pharmacokinetic targets for their patients
Additionally, in the first year, the proportion of patients achieving the desired therapeutic antibiotic range increased from 52% to 79%, an improvement of 27% from baseline.
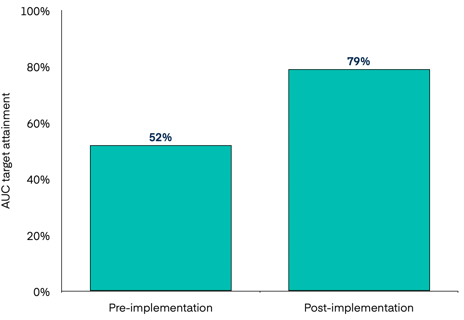
Figure 2 shows AUC target attainment pre- and post-implementation of Bayesian MIPD with InsightRX Nova for vancomycin AUC dosing.
Conclusion
Boone County Hospital’s success story illustrates that model-informed precision dosing is not reserved for large academic centers. With the right platform and implementation support, even small critical access hospitals can realize meaningful gains in patient safety, operational efficiency, and cost savings. Boone County’s experience provides a roadmap for other rural facilities aiming to modernize antibiotic dosing without adding undue burden.
This Success Story was adopted from a joint press release by Boone County and InsightRX, published in Healthcare IT News on August 25, 2022.




